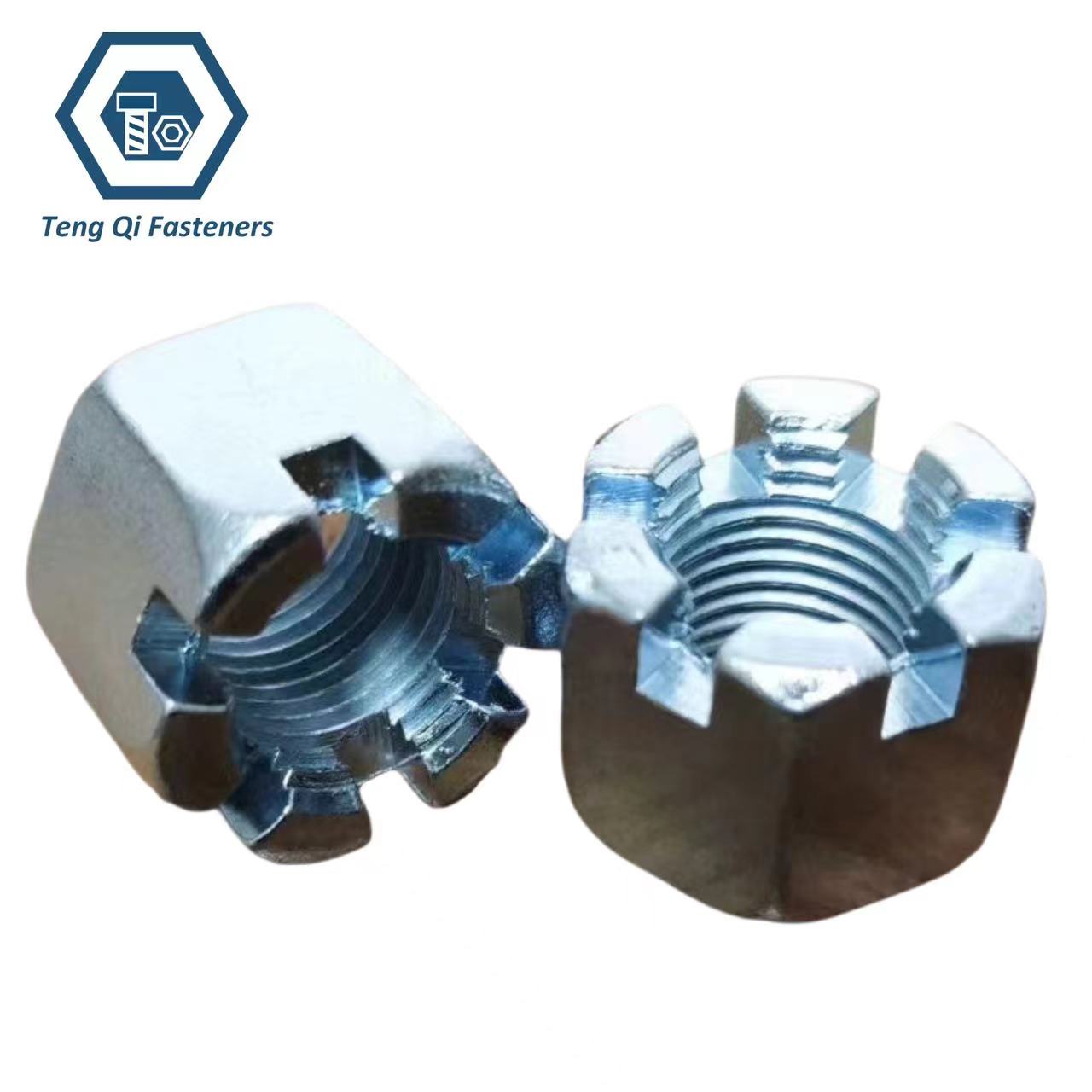
Slotted Nut Supplier In China
Ningbo Teng Qi Fasteners is a slotted nuts supplier in China. We specialize in the production of various slotted nuts, including DIN 935 slotted nuts, ASME B18.2.2 standard hex slotted nuts, hex thick slotted nuts, and heavy hex slotted nuts. Our extensive product lineup caters to a wide spectrum of applications, providing reliable solutions. Slotted nuts, also known as castle nuts or cotter nuts, are specialized types of nuts that have slots or openings cut into one end. These slots are aligned with a hole in the bolt or threaded rod they are fastened onto. The purpose of the slots is to allow for the insertion of a cotter pin or split pin, which prevents the nut from loosening unintentionally.
Slotted nuts are commonly used in applications where vibration or movement could cause regular nuts to loosen over time. The cotter pin holds the nut in place, ensuring that it remains securely fastened. These nuts are often found in automotive, machinery, and other mechanical systems where safety and reliability are crucial.
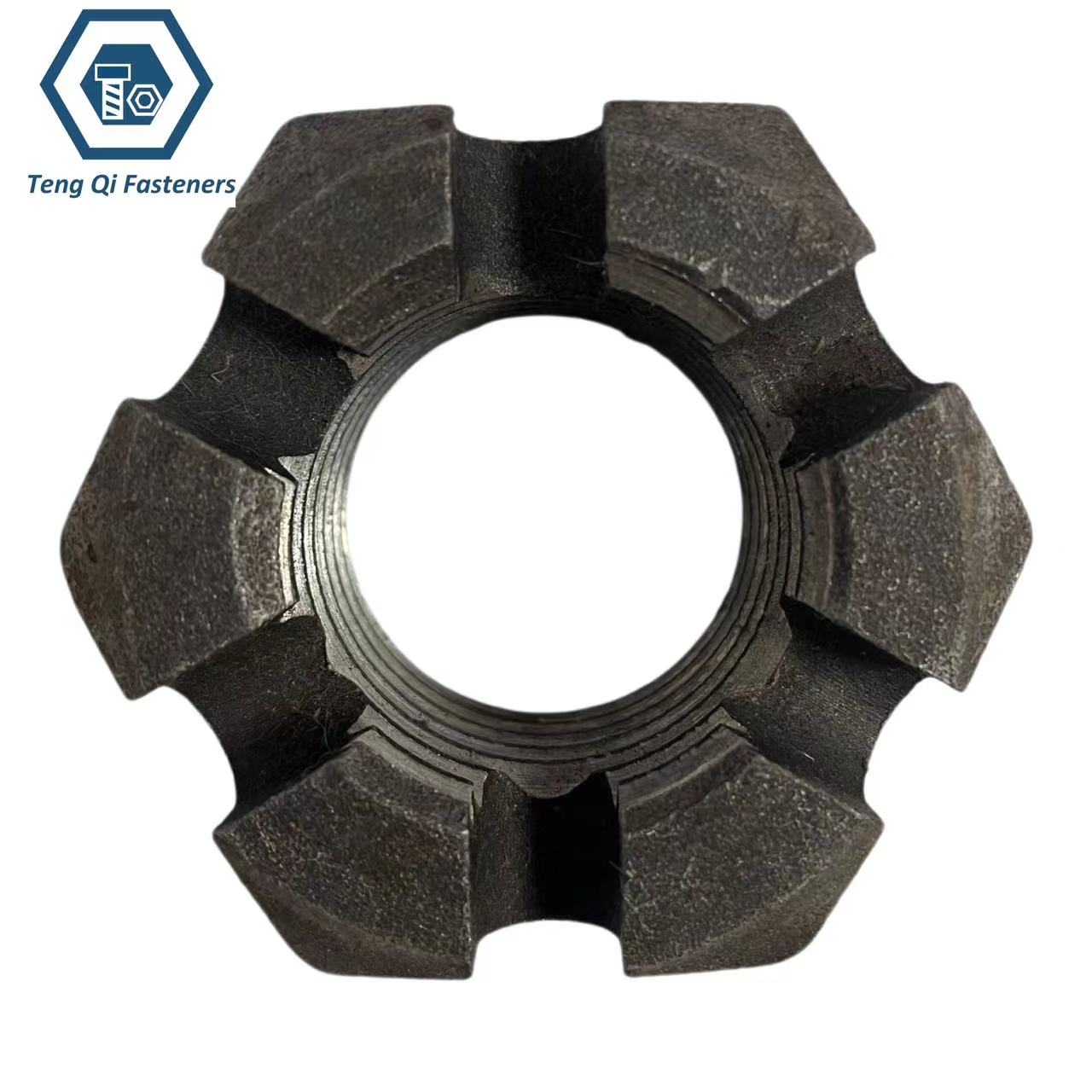

Specification of Slotted Nuts:
| Product name | Slotted Nuts |
|---|---|
| Diameter | Metric: M4-M100 Imperial:1/4" to 4" |
| Nut Class/Grade | ISO898-2: 5/6/8/10 SAE J 995: 2/5/8 A563/A194/F594 / F467 |
| Dimension Standard | DIN935/ASME B 18.2.2 |
| Material | Steel/Stainless steel/Brass |
| Type of Slotted Nut | Hex Slotted Nuts/ Hex Thick Slotted Nuts /Heavy Hex Slotted Nuts |
| Surface treatment | Black Oxide Coating/Zinc Plating /Mechanical Galvanizing/Dacromet Coating/Painting or Powder Coating |
Production Process of slotted nuts:
The production process of slotted nuts/castle nuts involves several steps to ensure quality and precision. Here’s a general overview of the manufacturing process:
- Material Selection: The process begins with the selection of appropriate materials based on the application requirements. Common materials for slotted nuts include carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, depending on factors like strength, corrosion resistance, and environmental conditions.
- Cold Heading/Hot forging: Hex nuts are first formed by cold heading or hot forging process.
- Slotting Cutting/Milling: After forming the basic shape of the nut, the slots are cut into the sides of the nut. This can be done using various methods such as milling, cutting.
- Heat Treatment (Optional): Depending on the material and the desired properties of the nut, heat treatment may be performed to improve hardness, strength, and proof load.
- Surface Finishing: Once the slots are cut and the heat treatment is completed (if necessary), the nuts may undergo surface finishing processes such as electroplate to enhance corrosion resistance, appearance, and durability.
Application:
| Industry | Details |
|---|---|
| Automotive Industry: | Castle nuts are commonly used in automotive applications, especially in suspension systems, steering components, and wheel assemblies. They provide a secure connection and allow for easy access for cotter pins or safety wires to prevent loosening. |
| Construction: | In construction, hex slotted nuts are used in structural assemblies where vibration and movement may occur. They are often found in scaffolding, bridges, and other steel structures. |
| Machinery and Equipment: | Castle nuts are employed in machinery and equipment assembly, particularly in rotating parts like axles, bearings, and shafts. The slotted design enables easy installation and removal while ensuring a tight fit. |
| Agricultural Equipment: | Hex slotted nuts are widely used in agricultural machinery for securing various components such as blades, gears, and linkages. Their design allows for quick adjustment and maintenance in the field. |
| Marine Applications: | In marine environments, where corrosion resistance is crucial, stainless steel hex slotted nuts are often used. They are found in boat engines, rigging, and other marine equipment. |
| Railroad and Transportation: | Hex slotted nuts play a role in railroad and transportation equipment, securing components such as rail tracks, couplings, and brake systems. |
Manufacturing quality control of of slotted nuts:
| Control Method | Detail |
|---|---|
| Material Inspection: | Verify the material's composition, heat treatment, and quality upon receipt. Conduct metallurgical analysis to ensure the material properties meet the standards. |
| Process Control: | Implement strict process control measures for heat treatment, machining, threading, and any other manufacturing steps. Maintain consistent process parameters to ensure uniform quality. |
| Inspection Points: | Introduce inspection points at various stages of manufacturing to check for defects, dimensions, and quality. Inspect threading, dimensions, surface finish, and other critical parameters. |
| Sampling and Testing: | Regularly sample products for testing, such as tensile testing, hardness testing, and metallurgical analysis, to ensure they meet the required specifications. |
| Thread Inspection: | Thoroughly inspect threading using proper thread gauges to ensure accurate dimensions and fit with mating components. |
| Traceability: | Implement a traceability system to track each fasteners journey from raw material to final product. This aids in accountability and recalls if necessary. |